A company needs to provision a secure and scalable AWS environment for public-facing workloads. The goal is to automate the creation of a network and compute resources using Terraform, following best practices and clear requirements.
Architecture Overview
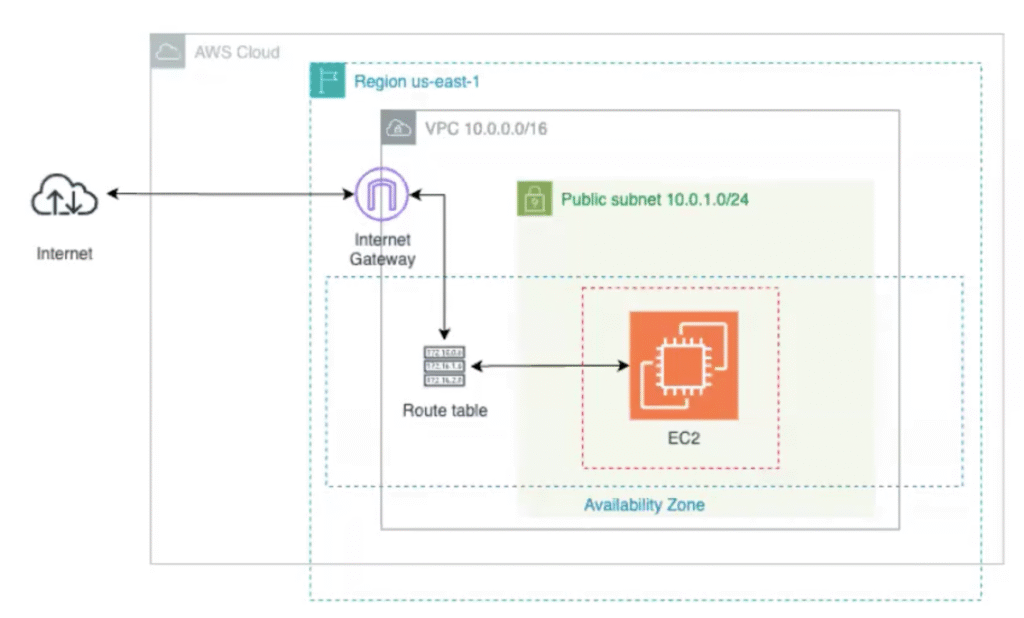
The solution provisions the following AWS resources:
- Custom VPC with a defined CIDR block
- Public Subnet associated with the VPC
- Internet Gateway attached to the VPC for outbound/inbound internet access
- Route Table with a route to the Internet Gateway, associated with the public subnet
- Security Group allowing inbound SSH (port 22) and all outbound traffic
- EC2 Instance (t2.micro) launched in the public subnet
- S3 Bucket (to be created manually) for storing the Terraform backend state
Below is the architecture diagram for reference:
Definition of Done (DoD)
This solution fulfills the following requirements:
- A custom VPC is created with its own CIDR block.
- At least one public subnet is defined and associated with the VPC.
- A public route table is configured with a route to the Internet Gateway.
- An Internet Gateway is implemented and attached to the VPC.
- A Security Group is created to allow SSH traffic (port 22).
- An EC2 instance (t2.micro) is launched in the public subnet.
- An existing SSH key can be used for access, or it is documented if omitted for simplicity.
Prerequisites
- Terraform installed
- AWS CLI configured
- LocalStack for local AWS emulation
Quick Start
- Start LocalStack:
localstack start -d - Set environment variables:
export AWS_ENDPOINT_URL=http://localhost:4566 export AWS_ENDPOINT_URL_S3=http://s3.localhost.localstack.cloud:4566 export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=test export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=test export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-1 - Initialize Terraform:
terraform init - Apply the configuration:
terraform apply
Note: Manually create the S3 bucket for the Terraform backend before running
terraform apply.