This project implements a CI/CD process using Jenkins, GitHub webhooks, and a Node.js API. Ngrok is used to publicly expose Jenkins, allowing GitHub to automatically trigger the application’s installation, testing, and deployment process.
Objective
To automate the CI/CD process, which includes installing dependencies, running tests, and deploying the application whenever a push or pull request is made to the repository.
Prerequisites
- A running Jenkins instance.
- Ngrok installed.
- A GitHub account and a fork of the repository.
- Jenkins plugins installed:
- GitHub Plugin
- NodeJS Plugin
- Configuration of the Node.js tool in Jenkins (under Tools). Ensure that the name used (e.g.,
nodejs) matches the pipeline configuration.
Step-by-Step Configuration
1. Configure Node.js in Jenkins
- Go to Manage Jenkins > Tools.
- In the NodeJS section, add a new installation.
- Assign it the name
nodejsand select the appropriate version.
2. Fork the Project
- Fork the repository on GitHub.
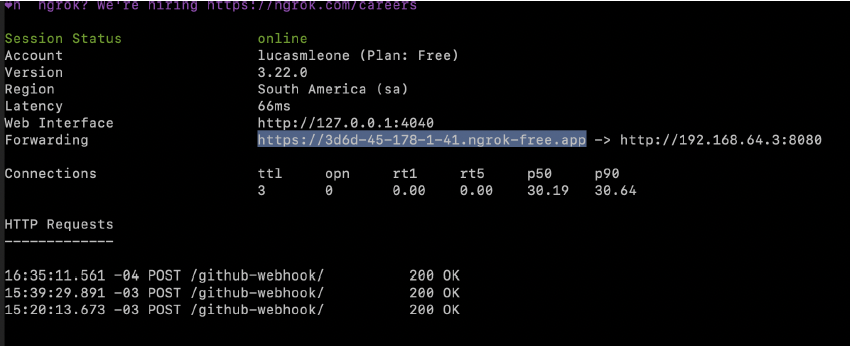
3. Expose Jenkins with Ngrok
- Start Ngrok to expose Jenkins on port 8080:Bash
ngrok http http://<your-ip>:8080 - Example generated URL:
https://random.ngrok-free.app/github-webhook/
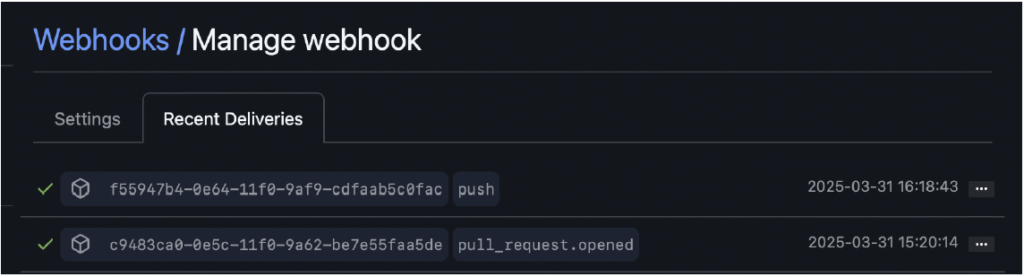
4. Configure the Webhook on GitHub
- Go to the forked repository on GitHub.
- Navigate to Settings > Webhooks and click Add webhook.
- In the Payload URL field, enter the generated URL:
https://random.ngrok-free.app/github-webhook/ - Select Content type:
application/json. - Check the following events:
- Push
- Pull request
Upgrade to a Multibranch Pipeline
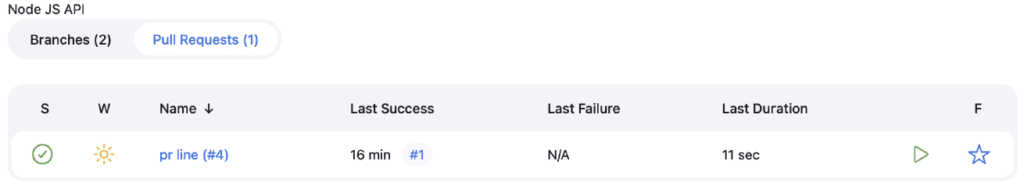
Initially, a classic pipeline was used, but it was decided to upgrade to a Multibranch Pipeline to improve automation. This change allows for automatic detection of changes in all branches and executes the pipeline for each pull request, testing the changes before they are accepted or merged.
Configuration
- A Multibranch Pipeline was created in Jenkins and configured with the forked GitHub repository.
- Note: It is important to add credentials to the multibranch pipeline, even if the repository is public. This helps increase the hourly usage limit of the GitHub API and avoids potential throttling.
- In the GitHub webhook, the option was enabled for the trigger to notify Jenkins whenever a new pull request is created in the repository.
- Jenkins now automatically detects changes in each branch and runs the pipeline, simulating the process as if the changes had already been merged.
How to Test the Process
- Make a push or create a pull request on GitHub to trigger the webhook.
- Jenkins will automatically run the CI/CD process.
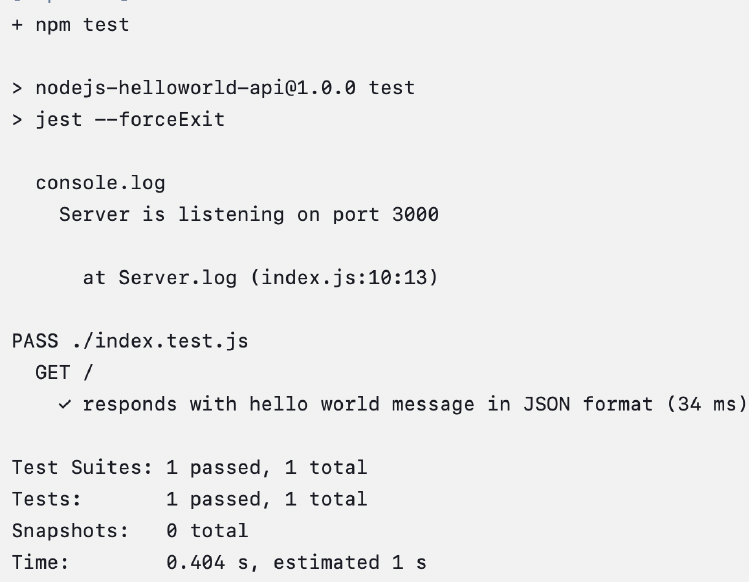
- Verify in the Jenkins interface that the process runs correctly by checking the logs for each stage (dependency installation, test execution, and application deployment).
Ngrok working
Webhook history
Pull request
Building pipeline
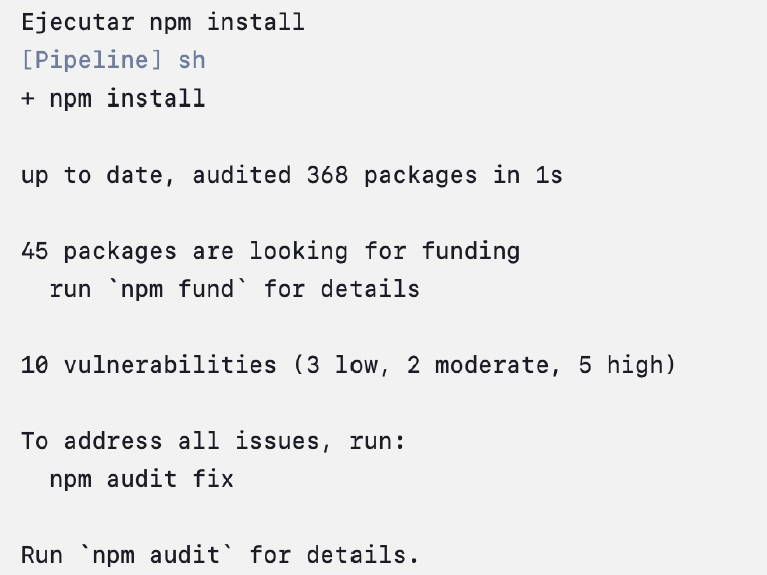
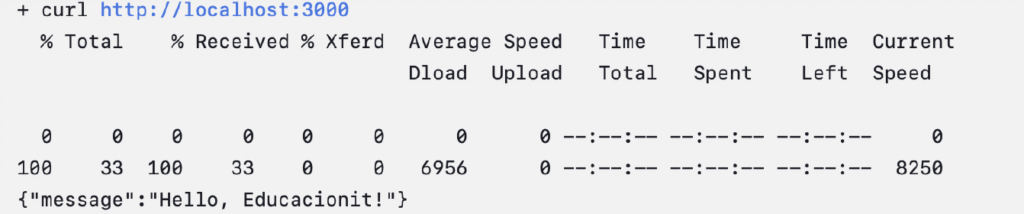
Testing
Health check